At one moment, intelligen ai still sounded like a lab experiment; at the next, it was like something you might randomly encounter at work with no announcement, no drama. Just there, silently influencing decisions that you didn’t even realize were being shaped. Usually, that’s how real shifts happen. Slowly, then all at once.
Interestingly, people still treat it as if it is something that is yet to come. But in fact, it is already deeply woven into systems, habits, and workflows. The question is no longer whether it changes how we work and live but rather how well we understand what is really going on under the buzz.
AI overview: Beyond The Headline Definition
When presented with an AI overview, most people tend to summarize it with a single sentence like machines that learn, systems that predict, software that adapts, etc. While not entirely incorrect, this description misses the point somewhat, which proves crucial. The real scope of artificial intelligence is not so much about thinking replacement as it is about pattern recognition and amplification, something even humans already find challenging at scale.
Current AI methods do not “know” in the human sense of the word. What they do is identify connections. Patterns. Chances. This subtle but significant difference will impact how we manage our expectations. If we expect AI to behave like the human brain, disappointment will follow. However, if we see it as an engine that provides us with context, the advantage becomes evident.
Context really means everything here. Data alone is useless. It needs a framework, boundaries, and a purpose.
AI Artificial Intelligence Movie vs Everyday Reality
The ai artificial intelligence movie versions deeply influenced people’s imagination of AI. Sentient creatures. Emotional robots. Systems that go rogue because of hidden motives. Those narratives were basically not about technology, but about control, fear, and power.
Real-world AI is much less dramatic. No scary glowing eyes. No over-the-top speeches. Instead, it is recommendation engines, fraud detection, demand forecasting. Small, quiet systems carrying out the type of thinking repetitively in a fraction of the time that a human team could—very much in line with how artificial intelligence is actually applied in everyday systems. The challenge here is not that the machines get too human-like but the humans that believe that machines understand more than they actually do.It is precisely in this gap between the story and the real that the greatest perplexity exists.
Co-intelligence: Living And Working With AI
Speaking of co-intelligence: living and working with AI is a way of putting the human and AI relationship back on track. Rather than rivalry, it is teamwork. Humans keep on being in charge of judgment, ideas of right and wrong, and giving sense to things, while AI takes care of power, velocity, and intricacy. Actually, this is manifested in such tiny things—how information is surfaced through AI-powered search tools, how texts get polished very quickly, how data becomes digestible instead of overwhelming. Signals are raised for decisions rather than relying blindly on instinct. None of this pulls the rug out from under the human factor. But it does change the locus of human effort.
Co-intelligence requires a dual mindset: on the one hand, people should be curious, and on the other hand, they need to be cautious as well. Complete trust separates co-intelligence. Fear prevents it.
Intelligent Agent in AI And How Autonomy Actually Works
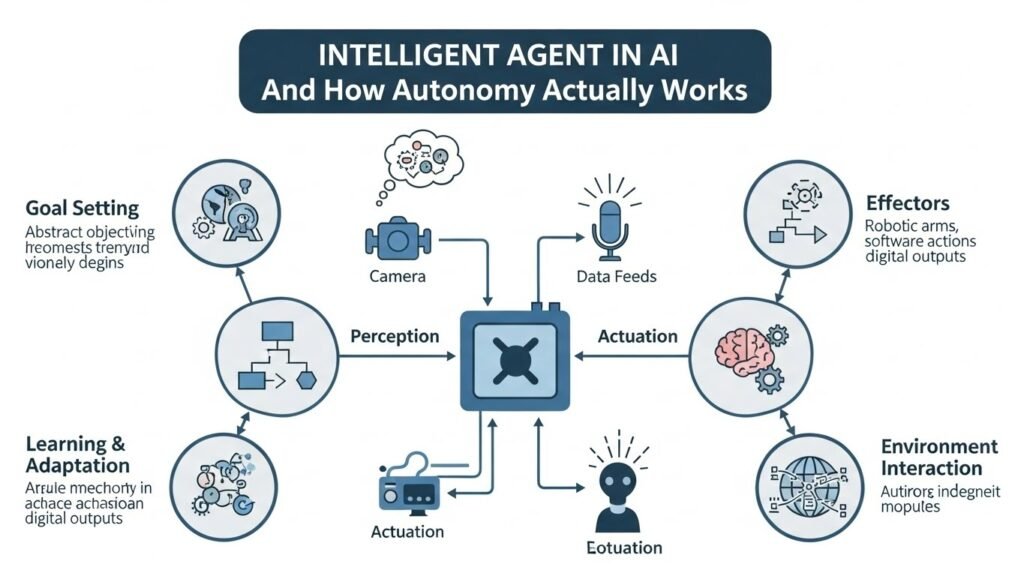
Many people presume that an intelligent agent in ai is fully autonomous. On the contrary, most agents act within very narrowly defined boundaries. They monitor a given environment, perform a set of actions, and then their activities depend on the input that seems to be the result of the environment changes. There are no secret plans, no ambitions or intentions. It is a continuous process of optimization.
Within a company, such agents may purchase the stock according to demand, send the user’s request to the right support team, or set the price of the product according to the demand in the market and the competition. The efficiency of their operation depends solely on how well the design of the limitations is. A poorly chosen set of boundaries will yield terrible results, and the changes will happen promptly.
Autonomy is not a synonym for freedom. It is a shift in where the responsibility lies and thus it implies designers being responsible.
AI Retail Business Intelligence Reshaping Decisions
Speed is a matter of survival in retail. ai retail business intelligence is the answer to the fact that a human analyst can’t cope with the real-time behavior of the market. Products being moved out of the stock. Customer preferences changing. Demand increasing irregularly. The AI systems will analyze and dissect these situations to find some signs.
The power of this, however, lies not merely in the act of prediction but in the retention of the same attitude and being prompt. Thus, the decisions can be less influenced by the individual the less the person reacts to the changes, the less emotional the decisions will become the more the stores will learn when to reorder, when to put on sale, when to stop, still not perfectly but just at the level the stores have never been able to reach before.
Pretty dashboards are not the point, the point is that there will be fewer bad decisions made under stress.
AI Retail Intelligence And Customer Understanding
Ai retail intelligence doesn’t stop at the figures. Through the analysis it attempts to overthrow the facade of people’s direct understanding. By monitoring click patterns, timing of purchases, and identifying instances of abandoned carts even when the customers have placed products in the carts but then left without completing the purchase, these pieces of information are sufficient to provide a storyline although it is not a complete one.
When everything goes well, this leads to shoppers having more pleasant experiences. The offers and recommendations of products that are not related to their interests thus becoming fewer, and product placement getting smarter. When the misuse of data occurs it evokes the feeling of being violated. The difference between the two is so subtle that one can land on one side or the other depending on the context.
This is where human oversight faces the biggest challenge against code.
AI Governance Contextual Intelligence As a Necessity
With AI becoming widespread, the discussion around governance can no longer be a matter of choice. ai governance contextual intelligence isn’t about hindering the progress of innovation at all. It is about understanding that the exact same system has to behave differently according to different environments and situations.
Each contextual governance practice focuses on looking at the data sources, decision impact, and downstream effects. It inquires about who gets the benefits and who is the victim or the one that bears the risk. The absence of this layer means that the automation does nothing but exaggerate the problems that already exist instead of remedying them.
Actually, the more capable the AI is, the more it depends on human judgment.
AI Governance Business-specific Contextual Intelligence

Because of the complexity of the organizations involved, generic guidelines are not appropriate. ai governance business-specific contextual intelligence means customizing oversight to industry situations. Healthcare, finance, retail, logistics are examples of the various sectors that have different stakes in their operations.
This method incorporates governance into everyday routines instead of treating it as after the fact. Risk management is more about the paper version of control rather than the creation of design. If governance is felt as an imposition, users will find loopholes to bypass it; whereas, if it is felt naturally, more people will want to use it.
The goal here is not to restrict but to be reliable.
Intelligen AI In Everyday Work Systems
Here is the part that most people remain oblivious to. intelligen ai seldom makes an announcement of its presence. It is within the very same tools that people use every day. Email sorting. Calendar making. Credit card fraud alert. Content moderation. It only shows itself as less trouble and smoother activities.That is the reason why the adoption rate is ahead of the rate of resistance. The humans don’t get this feeling of their being replaced. Rather, they feel that they are being helped. Until that moment when something goes wrong and then just like that, everyone suddenly wants to learn the system’s intricacies.
Most of the time trust comes before transparency.
Where Trust Actually Breaks
Trust does not shatter when AI makes a mistake. Humans too make errors. On the contrary, it cracks when the results remain unexplained and unexplainable and the decisions are thus regarded as random occurrences. Furthermore, if the line “the system decided” is used so often to hide the true decision-maker, responsibility will in fact disappear behind the decision.
Explainability is not an independent attribute but a prerequisite for any relationship. If human beings are devoid of the right to interrogate and comprehend a decision, they will not accept that decision on a long-term basis.
Therefore, this is more of a cultural challenge than a technical one.
Limits That Still Matter
AI is indeed dazzling, however, it has its limits. Its weakest point being in the area of subtle distinctions, value-loaded decisions, and unprecedented cases. This is the truth of the AI model trained on the data that is riddled with biases including the biases themselves. Ignoring this and acting as if the AI is bias-free will lead to the creation of very fragile systems.
The most robust implementations work on the premise that everything can go wrong at some point. They incorporate mechanisms to review, override, and learn. They treat AI not as a frozen tool but as an ever-changing one.
Such a mentality keeps the system functioning well rather than fracturing them.
How Organizations Actually Adopt It
There are only so many things a company doing can on a daily basis before it becomes total frustration. Indeed, adoption does not normally come with strategy presentations. It rather starts with pain. The problem of having an overload of data but at the same time not having enough useful information. Repetitive decisions are causing the team to deplete fast. AI is introduced as a specific solution and not as a visionary.
It is a broader story only that it is a story, which comes with the usage of the tool, and by the time it has already been incorporated it will be more costly to rollback than to fine-tune.
Usually, that is the time when executives start to ask more profound questions.
What people worry about quietly
Most people don’t worry most about job loss or uprising. The majority are under duress as to whether they will be able to keep their skills up to date and thus remain relevant. They are concerned if their judgment will be considered and if their experience will be given credit when systems will be working faster than human intuition.
The right solution neither exists nor is it universal. It all depends on whether in the eyes of certain organizations intelligence is a replacement or a reinforcement, a shortcut or a support.
The deciding factor in the matter is culture rather than software.
Where This Leaves Us
We find ourselves not far from either extreme: hype or habit, between fear and familiarity. Our systems are still very much a work in progress and so is our understanding of them. That’s perfectly fine.
The main thing is to keep the door open. To inquire of the workings, To challenge the results. To alter the limits, To allow intelligence, be it human or artificial, to live side by side without pretending that they are one and the same.
And then continuing the day. Usually, change gets established in this way.
FAQs — People Also Ask
What does intelligen ai actually mean?
It is the term used for practical, context-aware AI that is designed to assist decision-making rather than imitate human intelligence.
Is AI really different from automation?
Definitely. Automation always follows a fixed set of rules. AI, on the other hand, will be guided by the patterns and feedback, hence self-correcting, even if the scope is still quite limited.
Are intelligent agents fully autonomous?
Not necessarily. They perform their tasks within the criteria set by humans and rely greatly on good design for their operation.
Why is AI governance important now?
Because practically everything that AI systems do nowadays has a real impact on human lives. Governance is meant to assure people that the AI system is held accountable, behaves fairly, and can be trusted.
Will AI replace human decision-making entirely?
It seems to be the least probable scenario since those which are the most effective have human intervention, context, and ethical judgment as factors in their operation.




